The Future of Connected Vehicles: IoT & Telematics Trends 2024-2030
How vehicle connectivity is transforming automotive operations, customer experience, and mobility services
The connected vehicle market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by advancements in IoT technology, 5G connectivity, and increasing demand for data-driven services. By 2030, over 95% of new vehicles sold globally are expected to have some form of connectivity, fundamentally changing how vehicles are manufactured, sold, maintained, and used.
This comprehensive guide examines the current state of connected vehicle technology, emerging trends, and practical considerations for automotive enterprises planning their connected vehicle strategies.
Current State of Vehicle Connectivity
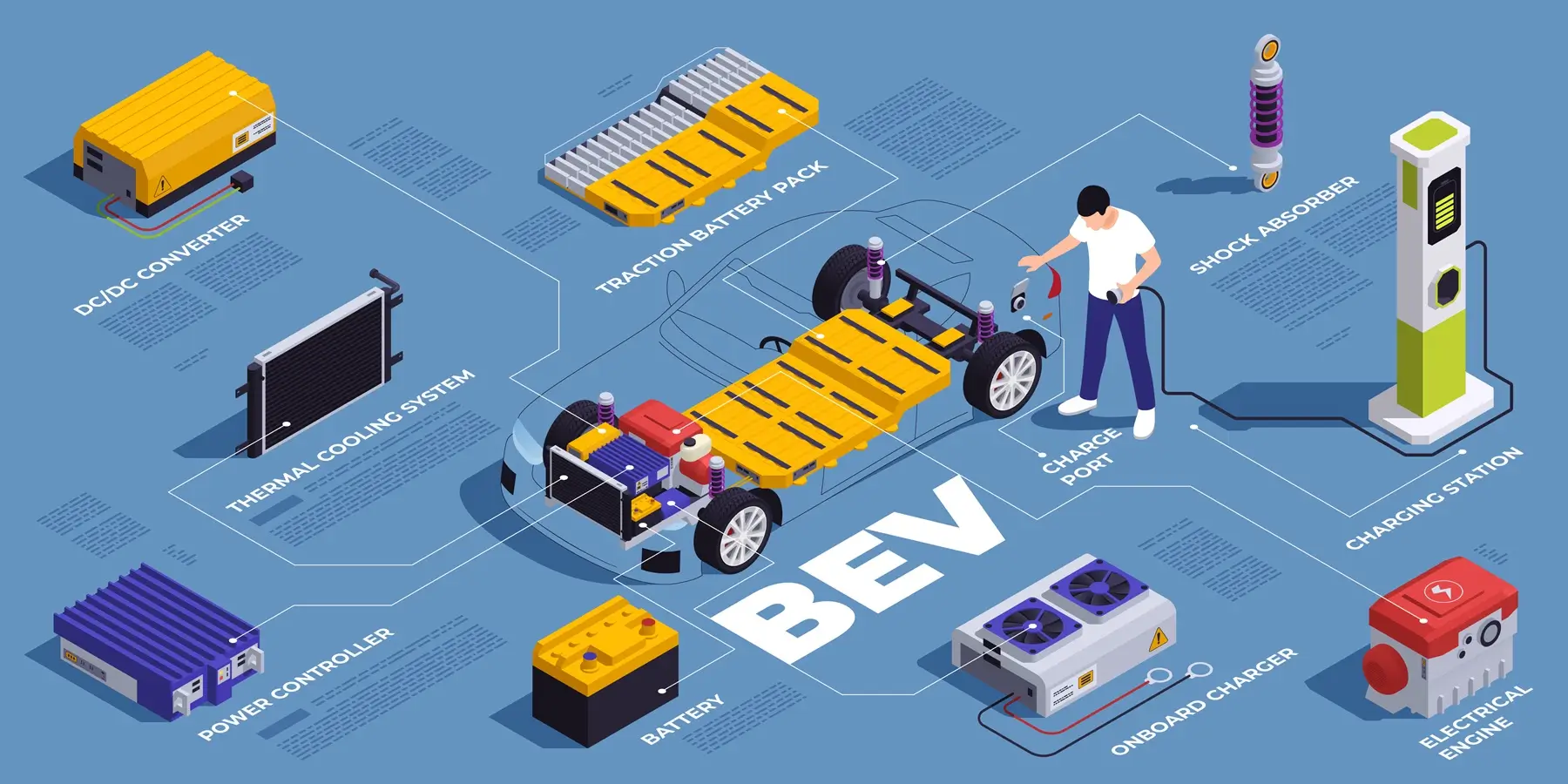
Today's connected vehicles leverage multiple connectivity technologies including 4G LTE, embedded telematics control units (TCUs), and OBD-II interfaces. These systems enable real-time vehicle diagnostics, over-the-air software updates, navigation services, and safety features like automatic crash notification.
The average connected vehicle generates approximately 25 GB of data per hour, creating opportunities for predictive maintenance, usage-based insurance, and personalized customer experiences. However, managing this data volume requires robust cloud infrastructure and analytics capabilities.
5G and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
5G networks are enabling new connected vehicle capabilities that were previously impossible with 4G. Ultra-low latency (under 10 milliseconds) supports real-time vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication for collision avoidance and cooperative driving. High bandwidth enables HD map updates and rich infotainment streaming.
V2X communication encompasses V2V, V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure), V2N (vehicle-to-network), and V2P (vehicle-to-pedestrian). These technologies form the foundation for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicle deployment.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA update capability has become a strategic priority for automotive manufacturers. Beyond fixing software bugs, OTA enables continuous feature improvements, security patches, and even performance enhancements throughout the vehicle lifecycle.
Successful OTA implementations require robust delta update technology to minimize download sizes, secure boot chains to prevent unauthorized modifications, and rollback capabilities for failed updates. The shift to software-defined vehicles makes OTA infrastructure increasingly critical.
Predictive Maintenance and Diagnostics
Connected vehicle data enables predictive maintenance that anticipates component failures before they occur. Machine learning models analyze patterns in engine telemetry, battery health, fluid levels, and driving conditions to predict maintenance needs.
For fleet operators, predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by up to 40% and extends vehicle lifecycle by 15-20%. For manufacturers, remote diagnostics reduce warranty costs and improve customer satisfaction through proactive service scheduling.
Data Monetization Opportunities
Connected vehicle data creates new revenue streams beyond traditional vehicle sales. Usage-based insurance (UBI) programs leverage driving behavior data for personalized pricing. Traffic data supports city planning and navigation services. Aggregated fleet data provides insights for infrastructure planning.
However, data monetization requires careful attention to privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA), transparent consent management, and robust data security. Automotive enterprises must balance revenue opportunities with customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful connected vehicle platform deployments share common characteristics: scalable cloud architecture that handles millions of connected vehicles, edge computing for latency-sensitive processing, comprehensive security frameworks, and flexible APIs for third-party integration.
Organizations should adopt a phased implementation approach, starting with core telematics capabilities before expanding to advanced features like V2X communication and autonomous functions. This allows for learning and refinement while managing investment risk.
Key Takeaways
- 95%+ of new vehicles will have connectivity by 2030, making connected vehicle strategy essential
- 5G enables V2X communication, creating foundation for ADAS and autonomous vehicles
- OTA updates transform vehicles from fixed products to continuously improving platforms
- Predictive maintenance reduces fleet downtime by up to 40% through proactive intervention
- Data monetization opportunities must be balanced with privacy and security requirements
- Phased implementation reduces risk while building organizational capabilities
Preparing for the Connected Future
The connected vehicle revolution is not coming—it's already here. Automotive enterprises that develop robust connected vehicle capabilities today will be positioned to capture value from new services, improve operational efficiency, and deliver superior customer experiences.
Success requires more than technology investment. Organizations must develop new capabilities in data management, cybersecurity, and customer engagement. The winners will be those who view connectivity not as a feature, but as a fundamental transformation of the automotive business model.
Filter by Categories
Table of Content
Years of Experience

